TẠI SAO BẠN NÊN ĐẦU TƯ SEO TỔNG THỂ?
SEO tổng thể là hình thức SEO đồng thời nhiều từ khóa (từ vài trăm – vài ngàn từ khóa) lên TOP Google. Giúp bạn tiếp cận tối đa tập khách hàng tiềm năng và tăng trưởng doanh thu.
Hình thức này khác biệt hoàn toàn với loại SEO từ khóa, thường chỉ tập trung vào số lượng ít từ khóa có lượng tìm kiếm cao, và tập trung chủ yếu vào các từ khóa sản phẩm, dịch vụ chính.
Ưu điểm của SEO tổng thể, giúp bạn tiếp cận được tối đa tập khách hàng ở mọi giai đoạn của hành trình mua hàng (buyer’s journey), tối đa hóa lượng truy cập tự nhiên, đem lại hiệu quả bền vững và an toàn qua thời gian.

PHƯƠNG PHÁP SEO PERFORMANCE

Chúng tôi phát triển và hoàn thiện kỹ thuật SEO Performance, dựa trên 3 kỹ thuật SEO độc quyền, giúp đem lại hiệu quả SEO vượt trội so với các phương pháp SEO truyền thống khác. Chúng bao gồm:
- Kỹ thuật gom nhóm từ khóa tự động hóa. Chỉ mất từ 5 – 10 phút, chúng tôi có thể gom nhóm hàng ngàn từ khóa, hình thành bản đồ Keyword Map, giúp SEO hàng trăm từ khóa chỉ trong duy nhất một bài viết, một cách hoàn toàn tự động với độ chính xác cao. Kỹ thuật này giúp bạn tiết kiệm tối đa chi phí, và tránh được tình trạng Keyword Cannibalization.
- Kỹ thuật xác định nội dung trọng tâm bằng dữ liệu lớn (big data) và phân tích ngược (reverse engineering). Kỹ thuật này giúp chúng tôi xác định loại nội dung trọng tâm mà cả Google và người dùng đều ưu tiên nhất, từ đó tập trung được nguồn lực để tối ưu vào những nội dung quan trọng nhất, đem lại vị trí từ khóa cao trên Google và tăng trưởng doanh thu.
- Kỹ thuật tìm kiếm và xây dựng backlink siêu chất lượng. Backlink siêu chất lượng đem lại sức mạnh vô cùng lớn, hiệu quả nhanh, an toàn tuyệt đối, chi phí chỉ bằng 30 – 50% so với loại backlink truyền thống. Với quy trình tìm kiếm độc đáo và hệ thống đối tác rộng lớn, chúng tôi dễ dàng xây dựng được những backlink siêu chất lượng mà đối thủ khó có thể mô phỏng và theo kịp.
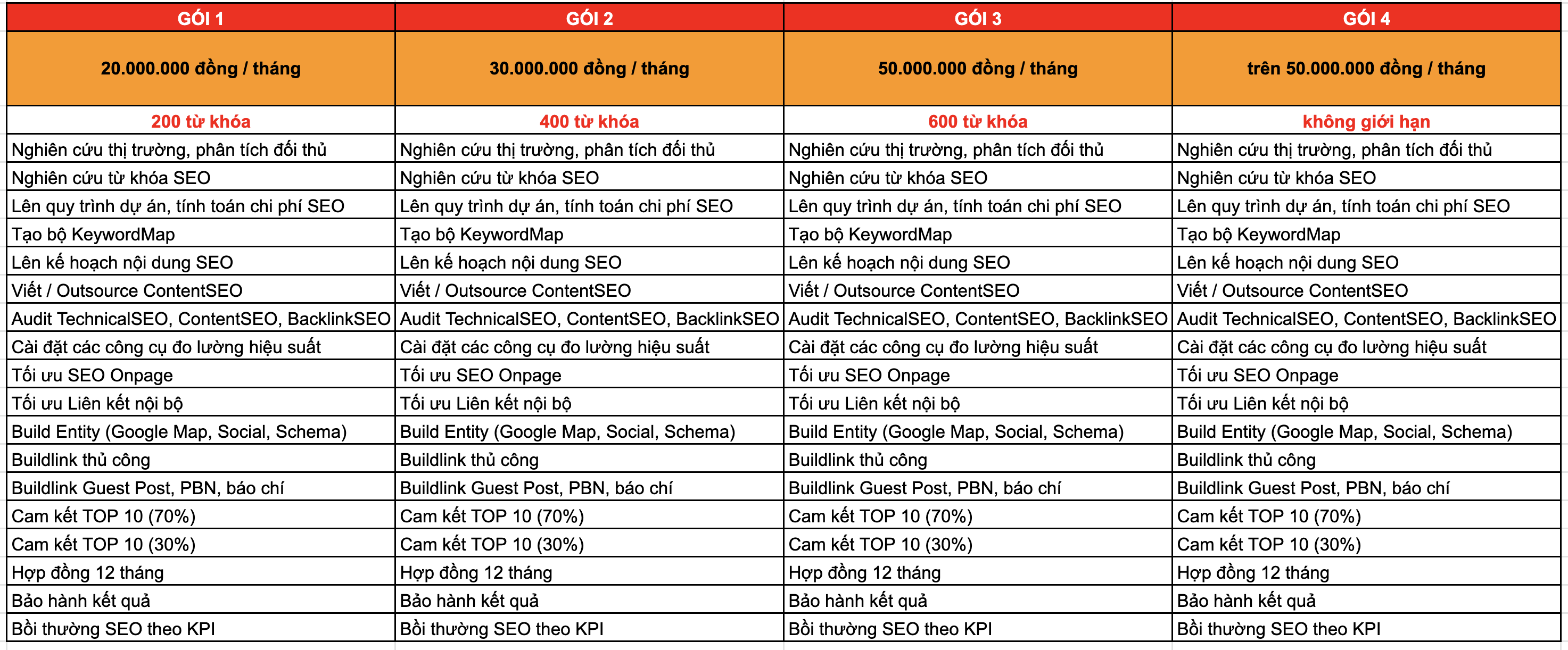
CÁC GÓI DỊCH VỤ SEO TỔNG THỂ
Dưới đây là các gói dịch vụ SEO tổng thể của chúng tôi.
QUY TRÌNH BÁO GIÁ SEO TỔNG THỂ
- Bước 1: Tiếp nhận yêu cầu của khách hàng
- Bước 2: Tư vấn SEO
- Bước 3: Lên KPI, kế hoạch SEO và bảng giá chi tiết
- Bước 4: Ký hợp đồng và thực thi dự án SEO
CÁC HẠNG MỤC TRIỂN KHAI
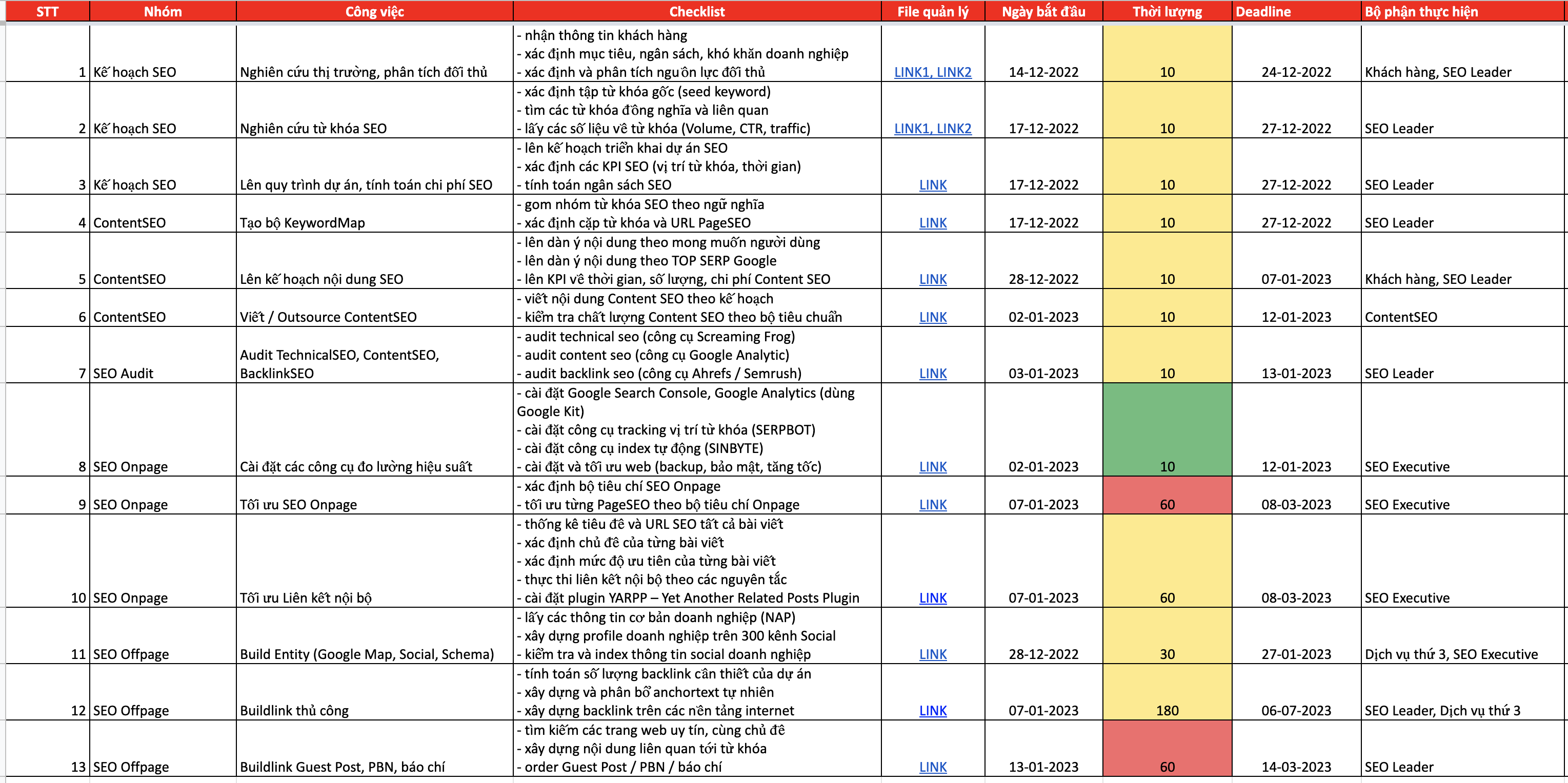
- Nghiên cứu thị trường, phân tích đối thủ
- Nghiên cứu từ khóa SEO
- Lên quy trình dự án, tính toán chi phí SEO
- Tạo bộ KeywordMap
- Lên kế hoạch nội dung SEO
- Viết / Outsource ContentSEO
- Audit TechnicalSEO, ContentSEO, BacklinkSEO
- Cài đặt các công cụ đo lường hiệu suất
- Tối ưu SEO Onpage
- Tối ưu Liên kết nội bộ
- Build Entity (Google Map, Social, Schema)
- Buildlink thủ công
- Buildlink Guest Post, PBN, báo chí
BẢO HÀNH VÀ CAM KẾT
- Chúng tôi có chính sách bảo hành kết quả SEO 3 tháng, và bàn giao toàn bộ nguồn tài nguyên SEO sau khi kết thúc dự án.
- Chúng tôi có chính sách bồi thường theo cam kết KPI ban đầu theo tỉ lệ hoàn thành tiến độ công việc. Nghĩa là, bạn chỉ trả phí cho những từ khóa đã đạt được đúng cam kết ban đầu.
CÁC DỰ ÁN ĐÃ TRIỂN KHAI
BẤT ĐỘNG SẢN

H là mô hình công viên nghĩa trang được xây dựng tại huyện Long Thành, Đồng Nai. Đây là mô hình nghĩa trang trung và cao cấp, với chất lượng dịch vụ tận tâm, có sổ hồng dự án, đảm bảo tính pháp lý, đồng thời đây cũng là một kênh đầu tư bất động sản có tiềm năng trong tương lai.
GIÁO DỤC ĐÀO TẠO

M là một trong những trường cao đẳng uy tín nhất Việt Nam. Với sứ mệnh góp phần vào việc xây dựng nền tảng nghề nghiệp vững chắc cho thế hệ trẻ Việt Nam không chỉ tại quê hương mà vươn ra tầm khu vực và thế giới, M mang đến cho người học các chương trình đào tạo có tính ứng dụng cao, cập nhật với nhu cầu của xã hội. Trường chuyên đào tạo các ngành thuộc Chăm sóc sức khoẻ, lĩnh vực kinh tế – dịch vụ, ngoại ngữ, thiết kế và CNTT. Ứng dụng theo chuẩn quốc gia và chuẩn quốc tế với phương pháp giảng dạy tiên tiến. Nhà trường chú trọng vào thực hành, thực tập trong từng môn học và nâng cao khả năng sử dụng ngoại ngữ cho sinh viên (đặc biệt là tiếng Anh).
LOGISTIC

Với phương châm hoạt động nhanh chóng – chính xác – an toàn – tiết kiệm, T là đơn vị vận chuyển với nhiều năm kinh nghiệm, đã từng cung cấp phát chuyển đi nước ngoài trên 200 quốc gia và vùng lãnh thổ trên thế giới: Mỹ, Canada, Úc, Đức, Trung Quốc, Đài Loan, Hàn Quốc, Nhật Bản, Macao, UAE, Singapore, Philipppines, Nga, Hongkong …sẽ mang đến cho bạn sự tin tưởng và hài lòng tuyệt đối. Cùng mức phí hợp lý, chuyển hàng nhanh, giao đúng người, đúng địa chỉ, và đội ngũ nhân viên chuyên nghiệp, trách nhiệm, T là đơn vị bạn hoàn toàn có thể an tâm tin tưởng.
ĐIỆN LẠNH

N là công ty hoạt động trong mảng điện lạnh, chuyên thu mua và buôn bán máy lạnh, tủ lạnh, máy giặt, tủ mát, tủ làm kem, điện lạnh công nghiệp. Ngoài mảng thu mua và buôn bán các thiết bị điện lạnh, công ty N còn cung cấp các dịch vụ sửa chữa, bảo hành máy lạnh, máy giặt tại nhà, lắp đặt và bảo trì máy lạnh, cho thuê và sửa chữa kho lạnh, thanh lý các loại tủ đông, tủ mát, tủ lạnh, tủ trưng bày bánh kem… Với gần 10 năm kinh nghiệm hoạt động trong mảng điện lạnh, cùng với đội ngũ nhân sự đông đảo và chuyên nghiệp, công ty N cung cấp dịch vụ điện lạnh với chất lượng dịch vụ cao, cùng với giá thành hợp lý nhất.
VẬN TẢI

D là một công ty chuyên cho thuê xe ô tô tự lái tại TP.HCM. Với phương châm “khách hàng là trên hết”, D không ngừng hoàn thiện sẽ đem đến khách hàng chất lượng và dịch vụ tốt nhất. D tập trung xây dựng một phong cách chuyên nghiệp, phục vụ mọi nhu cầu thuê xe ô tô của khách hàng, luôn giải quyết được mọi vấn đề xảy ra trong khi đang thuê xe cho khách hàng một các êm đẹp nhất và luôn cung cấp những dịch vụ, những chiếc xe chất lượng nhất khi tới tay khách thuê.
VĂN PHÒNG ẢO
Công ty Y được thành lập vào tháng 3 năm 2020, đây cũng là thời điểm bùng phát dịch COVID-19 và ảnh hưởng đến tình hình phát triển chung của các doanh nghiệp. Với sự quyết tâm và mong muốn đồng hành cùng các chủ doanh nghiệp, Startup trải qua 1 năm biến động, đầy thách thức và cùng nhau phát triển hơn trong thời gian sắp tới. Công ty Y mang đến các giải pháp văn phòng với mục tiêu “ TỐI ƯU CHI PHÍ – TỐI ĐA HIỆU QUẢ” và cũng là cộng đồng kết nối DOANH NHÂN đồng hành cùng PHÁT TRIỂN.
THỜI TRANG

B vốn là một cửa hàng nhỏ nhưng với kinh nghiệm 7 năm trong thị trường, hiện nay đã vươn lên trở thành nhãn hiệu thời trang đồ ngủ và đồ lót hàng đầu dành cho các chị em phái nữ. Đội ngũ nhân viên kinh nghiệm và tâm lý sẽ tư vấn chu đáo, nhiệt tình giúp khách hàng chọn được những món hàng thật ưng ý, hợp phong cách, vừa kích cỡ và chia sẽ cả cách bảo quản, giữ gìn để bộ trang phục luôn bền đẹp. Với phương châm hoạt động: Mang đến nụ cười hài lòng cho mỗi khách hàng khi bước ra từ cửa hàng. B sẽ luôn cố gắng hơn nữa để đem đến niềm tin và tình cảm của mọi chị em Phụ Nữ.
THIẾT KẾ THI CÔNG SÂN VƯỜN

Công ty thiết kế và thi công sân vườn V chuyên thực thi các dự án về thiết kế, thi công sân vườn, biệt thự, nhà hàng, quán café… Công ty Thiết Kế Sân Vườn V được thành lập từ năm 2013 với sứ mệnh đem lại những sản phẩm chất lượng tốt nhất tới quý khách hàng.
Đội ngũ nhân sự của chúng tôi được lãnh đạo bởi Kiến Trúc Sư (KTS) Đình Phong, cùng đội ngũ các kiến trúc sư, nhân viên thiết kế và đội ngũ thi công dự án với phong cách làm việc chuyên nghiệp, nhiệt tình, sáng tạo luôn nỗ lực để đem tới những giải pháp thi công sân vườn hiện đại.
Công ty Thiết Kế Sân Vườn V chuyên cung cấp các nhóm dịch vụ sau:
- Thiết kế thi công sân vườn
- Thiết kế thi công sân vườn biệt thự
- Thiết kế thi công sân vườn sân thượng
- Thiết kế thi công tiểu cảnh sân vườn
- Thiết kế thi công hồ cá koi
- Thiết kế thi công hòn non bộ
- Thiết kế thi công cảnh quan
- Thiết kế thi công quán cà phê sân vườn
- Chăm sóc bảo trì cảnh quan sân vườn
- Thiết kế thi công vườn rau trên sân thượng
- Thiết kế trang trí ban công
- Thiết kế thi công vườn tường đứng


